Códigos de modulación normalmente utilizados por radioaficionados:
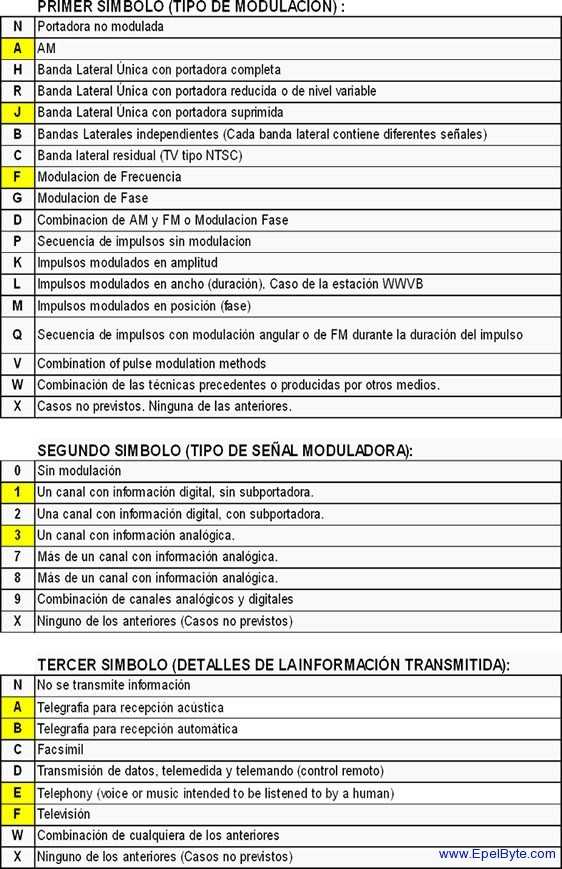
Algunos ejemplos:
| A1 | A – Double-sideband 1 – a single channel containing quantized or digital information without the use of a modulating sub-carrier | |
| A1A | A- Telegraphy – for aural reception | CW |
| A1B | B – Telegraphy – for automatic reception | CW |
| A1C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| A1D | D – Data transmission, telemetry, telecommand | CW(DSB) |
| A2 | A– Double-sideband 2– a single channel containing quantized or digital information with the use of a modulating sub-carrier | |
| A2A | A- Telegraphy – for aural reception | CW |
| A2B | B – Telegraphy – for automatic reception | CW |
| A2C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| A2D | D – Data transmission, telemetry, telecommand | |
| A3 | A– Double-sideband3– a single channel containing analogue information | |
| A3C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| A3E | E – Telephony (including sound broadcasting) | AM |
| F1 | F – Frequency modulation, 1 – a single channel containing quantized or digital information without the use of a modulating sub-carrier | |
| F1A | A- Telegraphy – for aural reception | CW |
| F1B | B – Telegraphy – for automatic reception | RTTY(FSK), SITOR-A, BAUDOT, FSK-Hell |
| F1C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| F2 | F– Frequency modulation, 2 – a single channel containing quantized or digital information with the use of a modulating sub-carrier | |
| F2A | A- Telegraphy – for aural reception | CW |
| F2C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| F2D | D – Data transmission, telemetry, telecommand | PACKED(FSK) |
| F3 | F – Frequency modulation, 3– a single channel containing analogue information | |
| F3C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| F3E | E – Telephony (including sound broadcasting) | FM |
| F3F | F – Television (video) | SSTV |
| G3 | G– Phase modulation, 3 – a single channel containing analogue information | |
| G3C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| G3E | E – Telephony (including sound broadcasting) | |
| G3F | F – Television (video) | |
| J2 | J – Single-sideband, suppressed carrier, 2 – a single channel containing quantized or digital information with the use of a modulating sub-carrier | |
| J2A | A- Telegraphy – for aural reception | CW |
| J2B | B – Telegraphy – for automatic reception | CW |
| J2C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| J2D | D – Data transmission, telemetry, telecommand | Clover |
| J3 | J – Single-sideband, suppressed carrier, 3 – a single channel containing analogue information | |
| J3C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| J3E | E – Telephony (including sound broadcasting) | SSB |
| J3F | F – Television (video) | ATV |
| R3 | R – Single-sideband, reduced or variable level carrier, 3 – a single channel containing analogue information | |
| R3C | C – Facsimile | FAX |
| R3E | E – Telephony (including sound broadcasting) | SSB |
Los más comunes podrían ser los siguientes:
A1A: ON/OFF keyed carrier (as in “CW” “Morse”)
A3E: double-sideband with full carrier (“AM”, “broadcast”)
J3E: single-sideband (“SSB”) suppressed carrier
F3E: frequency modulation telephony;
F2D: frequency shift keyed audio tone, data packet. Packet Radio.
Fuentes:
http://www.qsl.net/lz1iii/html/Modulation%20Codes.html
http://revistaqso.com/emision1.htm
